Calculate r-Value#
Contributor: Franz Roters
DAMASK version: 3.0.2
Prerequisites (data): DADF5 results file from MSC.Marc with plastic deformation gradient (‘F_p’)
Approaches to r-value calculations.#
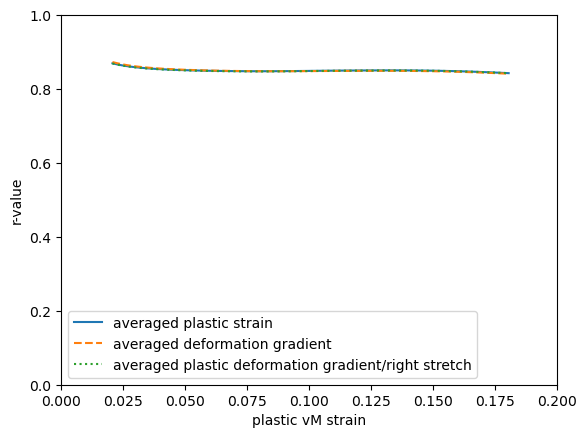
There are several options to calculate the strains that are used to calculate the r-value, the following are considered here:
Calculate the plastic strain \(\boldsymbol{\epsilon}_\mathrm{p}\) on each point before averaging
Average the deformation gradient \(\mathbf{F}\) and calculate the strain from this average
Calculate the right plastic stretch \(\mathbf{U}_\mathrm{p}\), average it, and calculate the strain from this average
Notes:
Averaging deformation gradients or stretches is preferred over averaging strains.
Differences between the use of \(\mathbf{F}\) and \(\mathbf{U}_\mathrm{p}\) are expected to be small because the elastic strains are small.
Since \(\mathbf{F}_\mathrm{p}\) contains rotation, averaging it or using strains based on \(\mathbf{V}_\mathrm{p}\) leads to bogus results (not shown here).
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
import damask
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[3]:
# adjust to your situation, file needs to exist
result_file = 'r-value_Marc/r-value_texture.hdf5'
[4]:
result = damask.Result(result_file)
result.add_strain('F_p','U')
result.add_stretch_tensor('F_p',t='U')
[5]:
# option 1, r-value from local plastic strain
epsilon_avegered = np.array([np.average(eps,0) for eps in result.get('epsilon_U^0.0(F_p)').values()])
r_eps_p = epsilon_avegered[:,1,1]/epsilon_avegered[:,2,2]
# option 2, r-value from averaged F
F_avg = np.array([np.average(F,0) for F in result.get('F').values()])
epsilon_avg = damask.mechanics.strain(F_avg,t='U',m=0.0)
r_F = epsilon_avg[:,1,1]/epsilon_avg[:,2,2]
# option 3, r-value from averaged U_p (F_p without rotational part)
U_p_avg = np.array([np.average(U_p,0) for U_p in result.get('U(F_p)').values()])
epsilon_F_p_avg = damask.mechanics.strain(U_p_avg,t='U',m=0.0)
assert np.allclose(epsilon_F_p_avg, damask.mechanics.strain(U_p_avg,t='V',m=0.0)) # no rotational part, so t='V' must be equivalent
r_F_p = epsilon_F_p_avg[:,1,1]/epsilon_F_p_avg[:,2,2]
epsilon_F_p_vM_avg = damask.mechanics.equivalent_strain_Mises(epsilon_F_p_avg)
[10]:
plt.plot(epsilon_F_p_vM_avg[10:],r_eps_p[10:],label='averaged plastic strain')
plt.plot(epsilon_F_p_vM_avg[10:],r_F[10:],label='averaged deformation gradient',linestyle='--')
plt.plot(epsilon_F_p_vM_avg[10:],r_F_p[10:],label='averaged plastic deformation gradient/right stretch',linestyle=':')
plt.ylabel('r-value')
plt.xlabel('plastic vM strain')
plt.axis([0, 0.2, 0, 1])
plt.legend()
plt.show()
[ ]: